This post explains the basic training structure in the UK. People who are interested to shift in the UK after MBBS by PLAB/MRCP and have dream to become a consultant there, must know these basic steps.
THE UK TRAINING PROGRAM
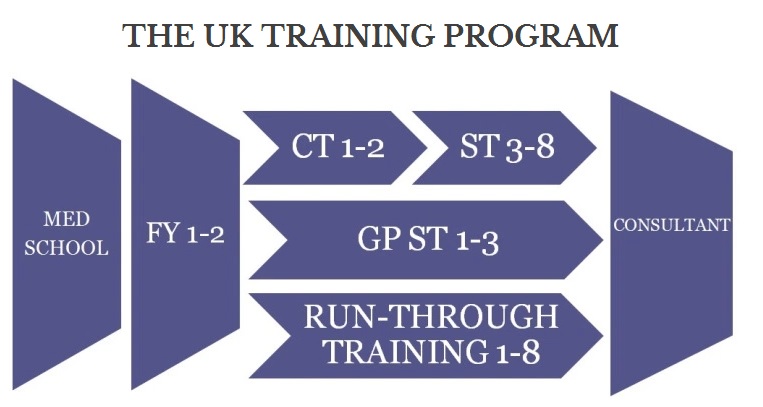
Training in the UK 1
Foundation Program
After graduating from medical school, there are two years of Foundation Program in the UK, known as F1 and F2. Foundation Program is also known as House Job or Internship in other countries.
Training Options After Foundation Program
To continue training after completing Foundation Program, there are different options. These are the common ones:
Core Training, followed by Specialty Training
GP Training
Run-Through Training
1. Core Training
Most people take this route. Core Training takes 2 years.
Core Medical Training
My friend, Dr. Omar Alam, has written about Core Medical Training application process in detail here.
Core Surgical Training
I don’t have any information about the Core Surgical Training or the opportunities in Core Surgical Training. If anyone could shed light on this subject, it
would help a lot of people.
Specialty Training
After completion of Core Training, passing MRCP/MRCS and meeting other eligibility requirements of Specialty Training, candidates can apply for Specialty Training. Specialty Training takes 5-6 years.
2. GP Training
A lot of people are coming towards this route now since the training is only for three years, there is no Core Training, the pay is good and working hours are easy.
You do not need to pass MRCGP to enter GP training. MRCGP can only be taken once GP training has begun for you.
3. Run-Through Training
Some specialties have a run-through training program. This means that the training would continue for a set period of time and the candidates would not have to apply for a training program again. Run-Through training takes 5-8 years.
The following specialties have a run-through program:
Chemical Pathology
Clinical Radiology
Community Sexual & Reproductive Health
General Practice
Histopathology
Neurosurgery
Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Ophthamology
Paediatrics
Consultant
All three roads will lead to you becoming a consultant.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are non-training jobs?
These are the jobs that IMGs with an acceptable pattern of internship should apply for. There can be many different titles to these jobs, but the jobs are nearly the same. These can include:
Foundation Year 2 (FY2)
Senior House Officer (SHO)
Core Training 1 (CT1)
Core Training 2 (CT2)
Specialty Training 1 (ST1)
Specialty Training (ST2)
Clinical Fellow (CF)
Junior Clinical Fellow (JCF)
Senior Clinical Fellow (SCF)
Junior Doctor
Trust Grade Doctor
It might confuse you seeing FY, CT and ST posts among non-training jobs. These jobs arise when a hospital needs FY, CT or ST Doctors, but it is not possible for them to recruit training doctors. So they hire non-training doctors for the same posts.
Working at these jobs will not count towards your training experience. However, the job description and the salary is the same as training jobs.
2. What is the difference between a training and a non-training job?
A training job is one in which there is career progression. In a non-training job, there is no career progression. Our internship (also known as House Job in Pakistan) and specialty training jobs (also knows as Residency in Pakistan) are training jobs.
3. What is F2 Competency?
Since IMGs do not go through UK’s Foundation training, they are required to get an F2 Competency form signed by their consultant. This form can be signed by any consultant, in the UK or in their home country, under whom they have worked for at least 3 months, during the last 3 years.
This form would not make them equivalent to candidates who have completed their Foundation training from the UK, but it would make them eligible to apply for Core Training program in the second round (First round is for British and EU citizens).
4. What is an Acceptable Pattern of Internship?
At least 12 months of internship with at least 3 months in medicine and at least 3 months in surgery is considered to be an acceptable pattern of internship. Medical and surgical sub-specialties count in medicine and surgery, respectively. For example, pediatrics and OBGYN are counted as medicine and surgery, respectively.
You must also check the official link from the GMC’s website to find out the acceptable patterns of internship.
5. Can I enter sub-specialty of my choice in Medicine?
You can visit the official ST3 recruitment website to check the number of openings for your preferred field. Go to the bottom of the page and click on your choice of sub-specialty. A new page will open. Click on Data. Check the number of openings for that field in round 2. This will give you an idea of your chances of making it to your choice of field.
You can also check competition ratios and seat availability from my post Training Availability in the UK.
Generally, entering non-surgical fields is very easy. Finding training in surgical fields require a lot of hard work and dedication in improving the CV. There is also tough competition over training spots in specialties like dermatology and radiology.
……………
Information Collected and edited by: Ferdous Rahman

