There are 4 heat related injuries :
1.Heat cramp
2.Heat syncope
3.Heat exhaustion
4.Heat stroke
In heat exhaustion and heat stroke, body’s core temperature also rise and serious consequence may arise.
Heat Cramps :
♦Painful muscle contractions occur due to profuse sweating in hot weather.
♦Symptoms usually respond rapidly to rehydration with oral rehydration salts or intravenous saline.
Heat Syncope :
♦Heat syncope or sudden collapse may result in unconsciousness from volume depletion and cutaneous vasodilation with consequent systemic and cerebral hypotension.
♦ Treatment consists of rest and recumbency in a cool place and fluid and electrolyte rehydration by mouth (or intravenously if necessary).
Heat Exhaustion :
♦ Heat exhaustion=Heat injury+increase core body temperature +Sweating present+Usually intact mental status.
♦ Blood analyses may show evidence of dehydration with mild elevation of the blood urea, sodium and haematocrit.
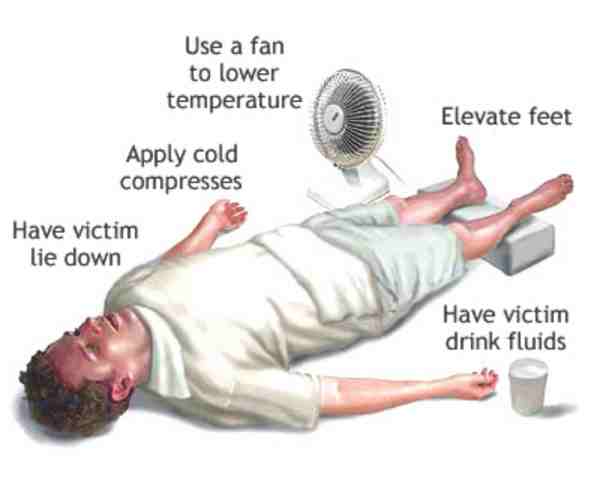
♦ Treatment involves removal of the patient from the heat, and active evaporative cooling using tepid sprays and fanning (strip–spray–fan). Fluid losses are replaced with either oral rehydration mixtures or intravenous isotonic saline. Up to 5 L positive fluid balance may be required in the first 24 hours.
♦ Untreated, heat exhaustion may progress to heat stroke.
Heat Stroke :
Heat stroke=Heat injury+Elevated body’s core temperature +absence of sweating+altered mental status
♦ The patient should be resuscitated with rapid cooling by spraying with water, fanning and ice packs in the axillae and groins. Cold crystalloid intravenous fluids are given.
Clinical Pearls :
1. Heat illness can be prevented to a large extent by adequate replacement of salt and water, although excessive water intake alone should be avoided because of the risk of dilutional hyponatraemia.
2. The cause is usually obvious but the differential diagnosis should be considered such as Malaria,Drug overdose, Thyroid strom,Malignant hyperpyrexia.
3. Solutions containing potassium should be avoided during fluid resuscitation .
4. Overaggressive fluid replacement must be avoided, as it may precipitate pulmonary oedema or further metabolic disturbance
5. Investigations are necessary usually only in heat stroke for complications identification including routine haematology and biochemistry, coagulation screen, hepatic transaminases (aspartate aminotrans ferase and alanine aminotransferase), creatine kinase and chest Xray.
Be Safe From Heatwave
Written By: Dr. Ashaduzzaman Kanak
Edited By: বনফুল

